[コンプリート!] club fungi sac fungi 208176-Club fungi and sac fungi differences
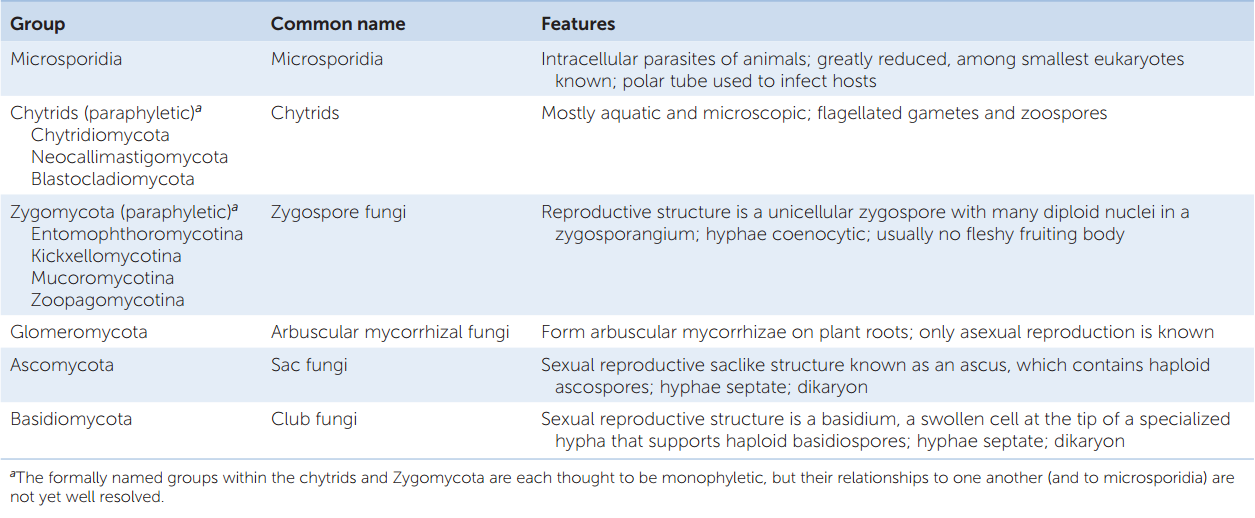
A feature is sexual spores in sacs (asci);Fungi Fungi are "eukaryotic heterotrophs with absorptive nutrition based on extracellular digestion' cell walls contain chitin Major fungal groups include the microsporidia, 'chytrids,' 'zygospore fungi,' arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, sac fungi, and club fungi" The members of the Kingdom Fungi are very important to life on earth Scientific Name Common Name Fungi Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Ascomycota Sac Fungi Glomeromycota Arbuscular mycorrhizai fungi and relatives Chytridiomycota Zygomycota Microscopic "Pin" or "Sugar" Molds Photographs Calphotos over 1,500 images of fungi, primarily Californian speciesa
Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home
Club fungi and sac fungi differences
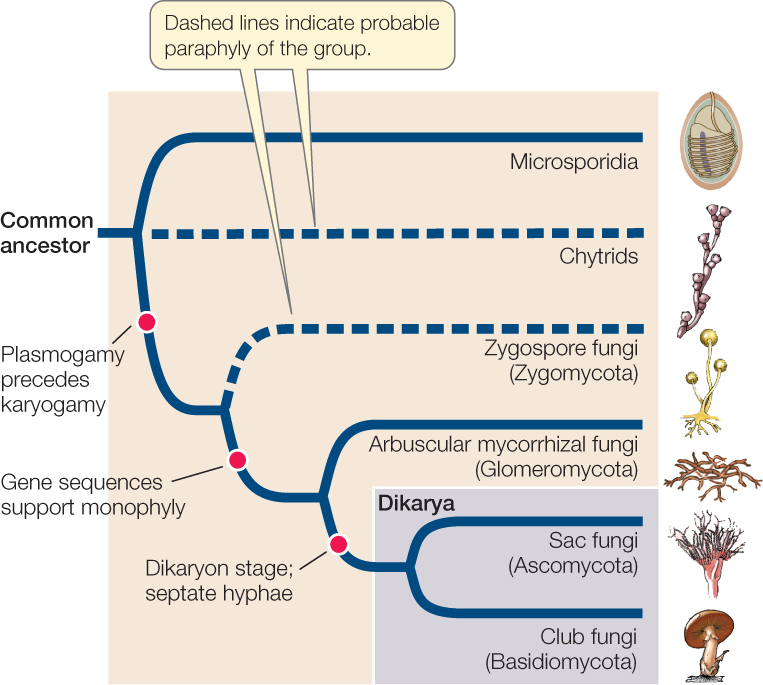
Club fungi and sac fungi differences- The traditional divisions of Fungi are the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), the Zygomycota(conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), and the Basidiomycota (club fungi) An older classification scheme grouped fungi that strictly use asexual reproduction into Deuteromycota, a group that is no longer in useThe five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recently described Phylum Glomeromycota The Deuteromycota is an informal group of unrelated fungi that all share a common character – they use strictly asexual reproduction




Ascomycota Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
What are common types of fungi? The club fungi are believed to be closely related to the sac fungi The club fungi reproduce asexually by producing asexual spores or by fragmentation of mycelium Similarly, what are club fungi named for? Kingdom fungi THE SAC FUNGI 1 Kingdom Fungi THE SAC FUNGI 2 Characteristics •STRUCTURE • Eukaryotic Heterotrophic (multi cellular decomposers) • with the exemption of YEAST • Multicellular fungi are composed of thin filaments called hyphae • hyphae tangled together into a thick mass called a mycelium 3
Features includes sexual spores in the basidiocarp (mushroom) and that they are mostly decomposers;Phylum – Sac Fungi Although the Sac Fungi are less familiar to most people this phylum is very important economically Yeast is a sac fungus used to make bread, beer, and wine Pencillium is a sac fungus that was the source of the first antibiotic and its close relatives are responsible for the flavor of cheeses such as Brie and Roquefort Basidiomycetes – The Club Fungi 1 Basidiomycetes (Gk basidium small base, mykes fungus) are the most advanced and most commonly seen fungi as their fructifications are often large and conspicuous, eg, mushrooms (gill fungi), toadstools, puff balls, bracket fungi, etc 2 The class contains about 25,000 species 3
Features includes sexual spores in the basidiocarp (mushroom) and that they are mostly decomposers;Correct answers 2 question Identify the fungus type pictured below club fungi sac fungi imperfect fungi zygote fungi Ascomycota (sac fungi) may have unicellular or multicellular body structure;




Fungi And Fungirl That Joke Never Gets Old




Ascomycota Wikipedia
A feature is sexual spores in sacs (asci); Ascomycota (Ascomycetes or Sac – Fungi) It is the biggest group of fungi, including over 60,000 species, 50% or so present in lichens, and some, such as morels, are mycorrhizal Most are terrestrial, though some are marine or freshwater The group shows diversity from unicellular yeasts to big cup fungi and morels Answer2sac fungiExplanationAscomycota The Sac Fungi The majority of known fungi belong to the Phylum Ascomycota, which is characterized by the formation of lulroxk59 lulroxk59 Biology Middle School Which is the largest group of fungi?




Fungi By Dominic Decarlo Brett Rosato And Brendan Beecher Chapter 30 Pptx Powerpoint




The Many Kinds Of Fungi
Examples include the yeasts used in bread, wine, and beer production Basidiomycota (club fungi) have multicellular bodies;When growing conditions where the land is right the sprore will become a fungus There are four main groups of fungi threadlike fungi, sac fungi, club fungi, and imperfect fungi The fuzzy mold growing on bread belongs to the group of fungi called threadlike fungi most of the fungi in this group live in the soil and are decomposersA/G Ratio (meaningful tests) A1c (glycated hemoglobin/red blood cells)
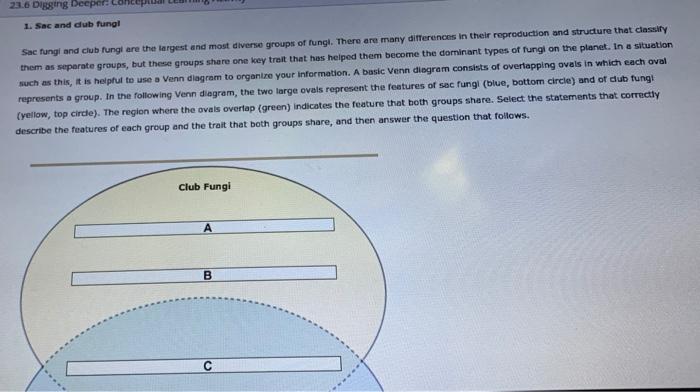



Solved 23 6 Digging Deeper Co 1 Sac And Club Fungi Sac Chegg Com



Fungi
The common mushrooms, puffballs, and truffles belong to the class of fungi called (a) Ascomycetes (b) Basidiomycetes (c) Zygomycetes (d) Deuteromycetes 30 The cause of thrush, yeast infection, and other maladies in humans is the fungus (a) Cryptococcus neoformans (b) Agaricus nigricansAscomycota (sac fungi) may have unicellular or multicellular body structure;Club fungi sac fungi zygote fungi




Hillis2e Ch22




Sac Fungi Hd Stock Images Shutterstock
Examples include the yeasts used in bread, wine, and beer production Basidiomycota (club fungi) have multicellular bodies;1 X Club fungi Y Zygote fungi Z Sac fungiBy sequencing the DNA of this and other strains and comparing them for similarities Damp weather increases the incidence of mildew fungal disease in plants because in damp conditions the stomata are open, giving the fungus easy access to plant leaf cells




8 17g Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology Libretexts




Characteristics And Major Groups For Fungi
Features includes sexual spores in the basidiocarp (mushroom) and that they are mostly decomposers;Please select from the menu above A/B/C template; The difference between club fungi and sac fungi is that sac fungi's spores are produced in sacs called asci However, club fungi's spores are produced in a clubshaped structure called a basidium



1



Fungi Humans Examples Body Parasites Used Water Process Earth
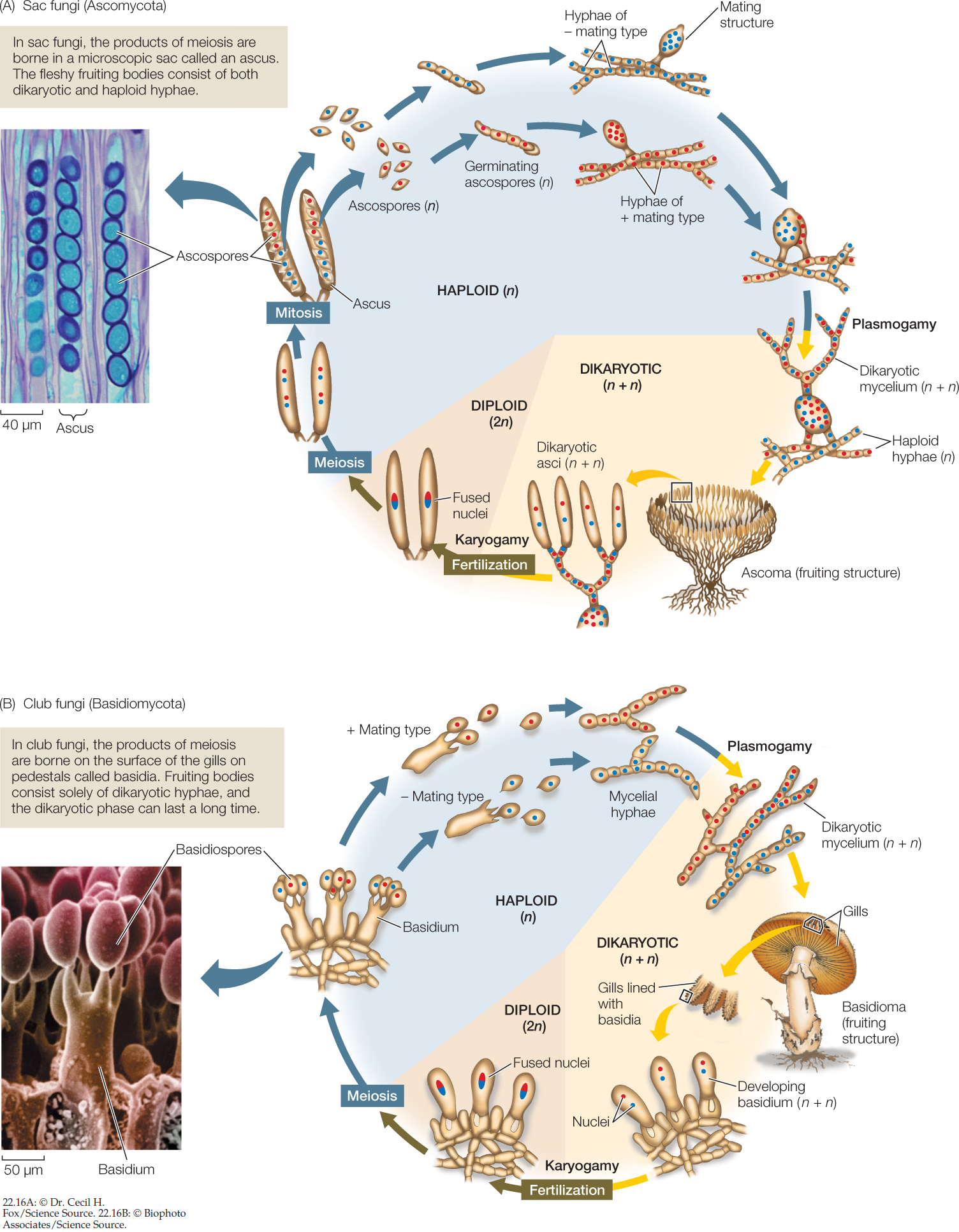
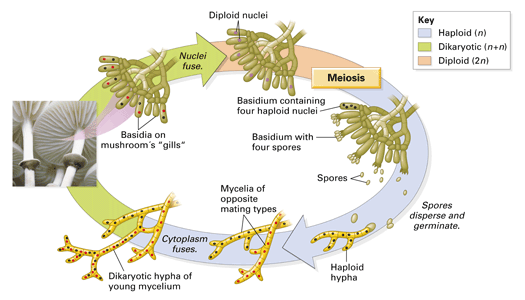
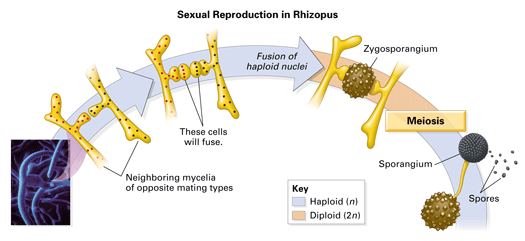
There are four major groups of fungi Zygomycota, Ascomycota (sac fungi), Basidiomycota (club fungi), and Deuteromycota (fungi imperfecti) The fungal group Zygomycota is most frequently encountered as common bread molds, although both freshwater and marine species existSac fungi, or ascomycetes, named for their phylum Ascomycota, is a group of fungi consisting of around 30,000 species They are sapotrophs which play an important ecological role by decomposing resistant materials containing cellulose, lignin, or collagen In sac fungi, their phylum name refers to the ascus (from the Greek askos, meaning bag orIn the two remaining groups of fungi—the sac fungi and the club fungi—some stages have a nuclear configuration other than the familiar haploid or diploid states (FIGURE 2216) In these fungi, karyogamy (fusion of nuclei) occurs long after plasmogamy (fusion of cytoplasm), so that two genetically different haploid nuclei coexist and divide within each cell of the mycelium




Sac Fungi Peziza Repanda Fungi Stuffed Mushrooms Mushroom Fungi




Characteristics Of Fungi Biology For Non Majors Ii
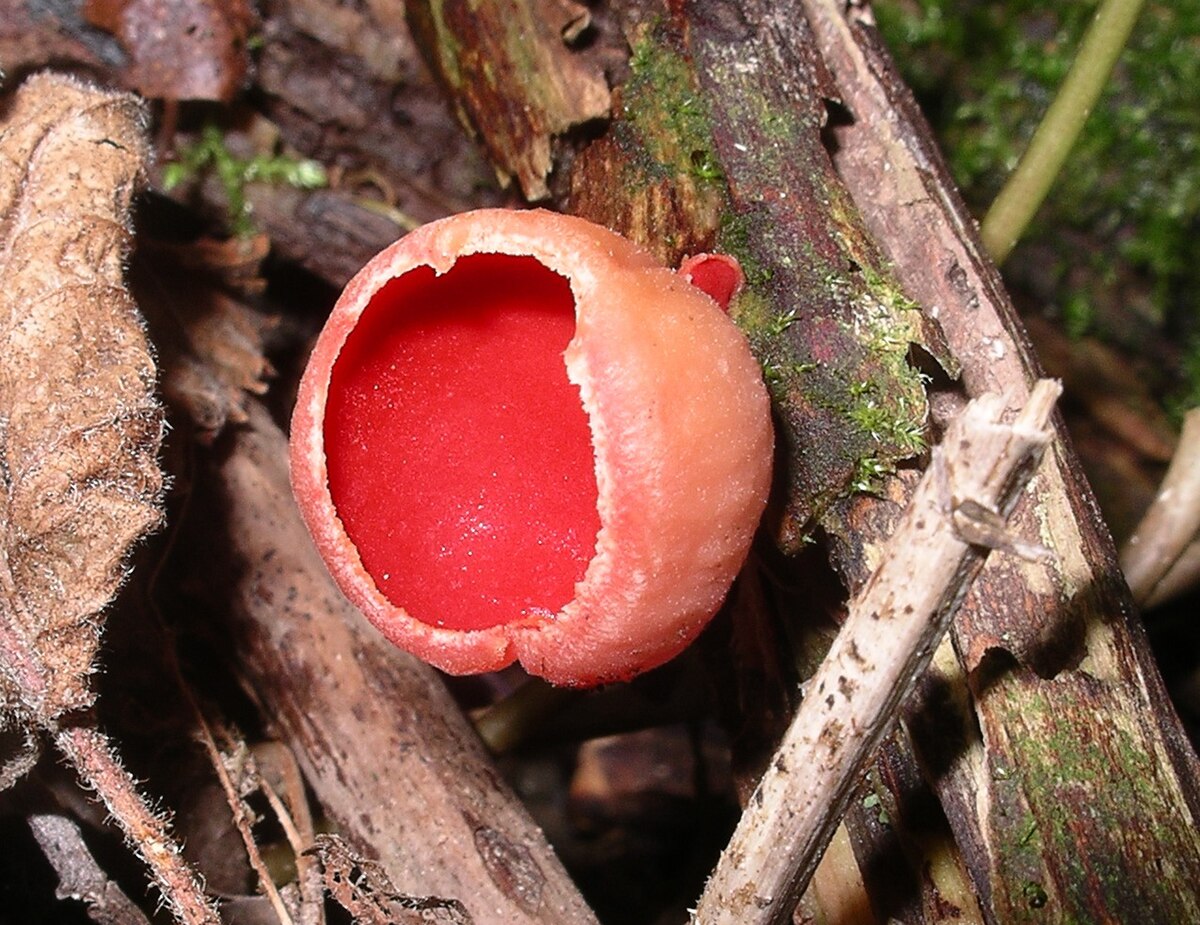
Club fungi can reproduce asexually, but sexual reproduction is more common They reproduce using spores Development Sac fungi grow hyphae from the spore The mycelia have a huge surface area Examples Some examples of club fungi include mushrooms, polypores, puffballs, boletes, and bird's nest fungiThe five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recently described Phylum Glomeromycota The Deuteromycota is an informal group of unrelated fungi that all share a common character – they use strictly asexual reproductionSac fungi Explanation The species of the figure is a fungus of the Ascomycota phylum (Sac fungi) belonging to the Pezizaceae family, whose characteristic is the production of mushrooms in a bowllike shape This shape allows the spores inside the mushroom to



Sac Fungi




The Reproductive Cycles Of Fungi Zoom Out Mycology
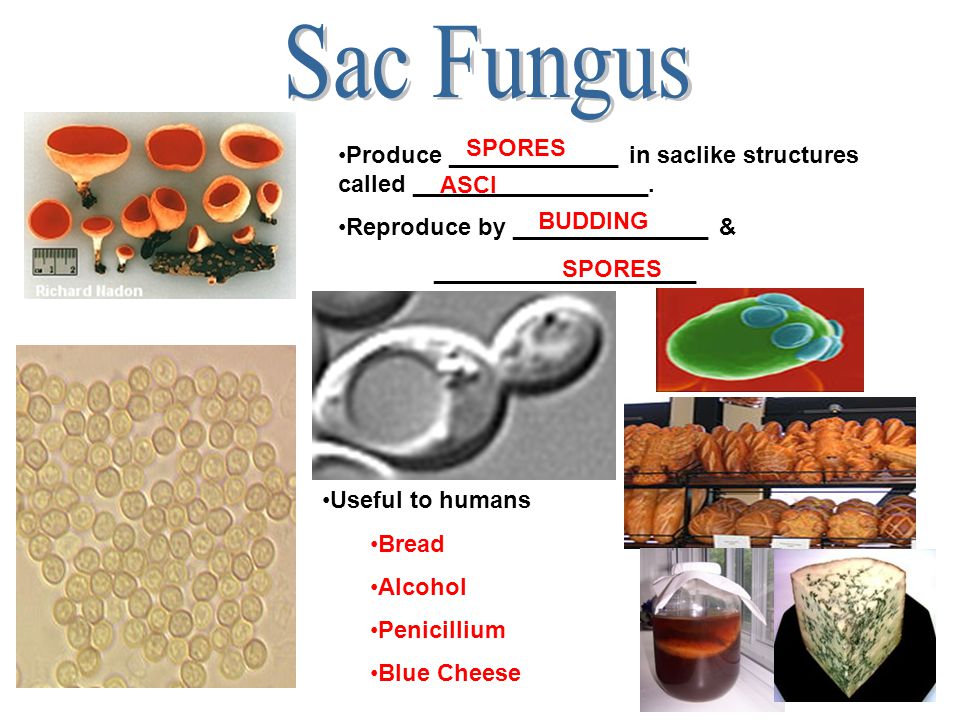
Ricardo listed characteristics of three types of fungi in a chart Which headings correctly complete the chart?The kingdom fungi are made up of lichen, yeast, mushrooms, and moldsTable Contents the Fungi Kingdom010 Introduction Kingdom Fungi023 Fungi Facts052 HowFungi are classified into four groups based on the way they reproduce sexually by producing nonmotile spores 1 Sac Fungi Sac fungi produce spores in cupshaped sacs, called asci which contain 48 ascospores This is the largest group of fungi




Fungus Chapter Ppt Video Online Download



Biology4kids Com Microorganisms Fungi
Phycomycetes are called algal fungi, Ascomycota was commonly known as the sac fungi, fungi imperfecti also known as Deuteromycota, The division of fungi known as the club fungi, Basidiomycota So, the correct option is 'A(ii), B(i), C(iv), D(iii)'Habitat Most club fungi are terrestrial Anatomical Structures and Features Club fungi are dikaryotic mycelia (they have cells with two nuclei) Mostly reproduce sexually, rarely asexually Most are multicellular Have a clubshaped special hyphae on the underside of their caps How do they acquire nutrients Sac fungi are heterotrophicClub Fungi Club fungi (Phylum Basidiomycota) are considered the most highly evolved fungi They are an important group with about 16,000 known species The phylum contains several subgroups whose relationships are not entirely clear One subgroup, the "higher" club fungi, includes those that produce large fruiting bodies such as mushrooms, puffballs, or woody



Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home



Toronto Wildlife Sac Fungi
Examples include the yeasts used in bread, wine, and beer production Basidiomycota (club fungi) have multicellular bodies; The Kingdom Fungi (or Mycota) is a group of living organisms that are multicellular, eukaryotic, and heterotrophic in nutrition Fungi live mostly as saprobiotic or often parasites Fungi show great diversity in morphology and habitat Study of Fungi The branch of biology which studies the various groups of fungi is known as Mycology The difference between club fungi and sac fungi is that sac fungi's spores are produced in sacs called asci However, club fungi's spores are produced in a clubshaped structure called a basidium




The Fungus Kingdom Chapter 5 The Fungus Kingdom




Identify The Fungus Type Pictured Below The Image Shows A Mushroom Used Often In Cooking Will Brainly Com
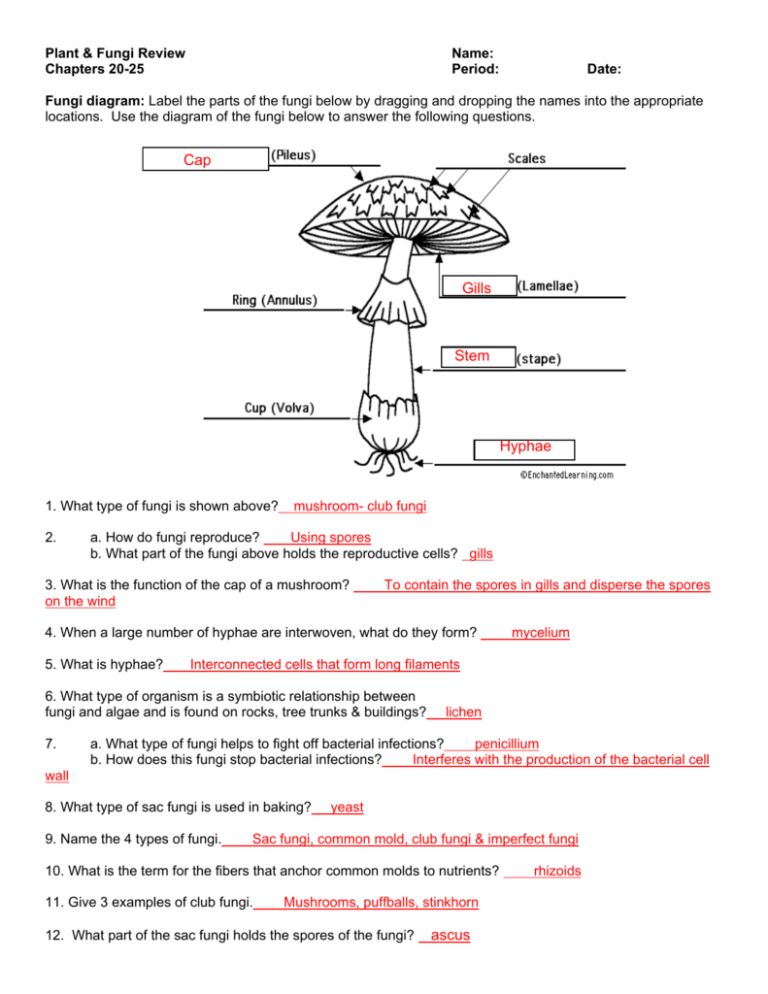
Club fungi are named for their clubshaped, sporeproducing structure called a basidium Ascomycetes (Sac fungi) They can be unicellular and multicellular fungi There are over 30,000 species of Ascomycetes (Sac fungi) They develop asexual spore exogenously in form of chains known as conidia They develop sexual spores in a saclike ascus These are endogenous ascosp ores The fruiting body containing asci is called ascocarpThe reproductive structure where spores develop on sac fungi Basidia spore cases of club fungi Budding A form of asexual reproduction of yeast in which a new cell grows out of the body of a parent Club Fungi This group consists of 25,000 members It includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, and puffballs Fission



What Is The Difference Between Ascomycota And Basidiomycota Pediaa Com




Ppt Ascomycetes Sac Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Ascomycota (sac fungi) may have unicellular or multicellular body structure;The image shows a mushroom used often in cooking, will gills underneath it's cap A Zygote fungi BImperfect fungi CSac fungi DClub fungi Biology 7 months ago Give Answer Answers AnswerThe correct option is D) club fungiExplanationThe club fungi includes most of the familiar types of mushrooms Imperfect fungi Sac fungi Club fungi search rotate 2 See answers report flag outlined bell outlined




Concept Check 18 Docx Concept Check 18 1 1 What Features Of A Mycelium Make It An Efficient Structure To Obtain Food By Absorption The Hyphae Of A Course Hero



2
Q Blue cheese and athlete's foot come from this kind of fungus that is named due to a lack of a "perfect" reproductive stage in their life cycle answer choices club fungi sac fungi imperfect fungi zygote fungiA feature is sexual spores in sacs (asci);Types of Fungi Scientists often divide fungi into four groups club fungi, molds, sac fungi, and imperfect fungi Some of the more common fungi that you are likely to see or use everyday are described below Mushrooms Mushrooms are part of the club fungi group Mushrooms are the fruiting body of a fungus




Fungi Sac Fungi Yeast Molds Rusts Smuts Fungi Discover Life Mobile




Do Fungi Get Enough Respect In Our Planet S Ecosystem The Riverdale Press Riverdalepress Com
The main difference between Ascomycota and Basidiomycota is that the Ascomycota includes sac fungi that produce spores inside a sac called the ascus whereas Basidiomycota includes club fungi the produce spores at the end of specialized cells called basidiaFurthermore, asexual reproduction is prominent in Ascomycota while sexual reproduction is prominent inBasidiomycetes are Commonly known as club fungi and known forms are mushrooms, bracket fungi or puffballs Ascomycetes are Commonly known as sacfungi, the ascomycetes are mostlymulticellular, eg, Penicillium, or rarely unicellular, eg, yeast(Saccharomyces) Some examples are Aspergillus, Claviceps, and Neurospora




Classifications Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e




8 17g Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology Libretexts




Fungi Plants Without Chlorphyll What Makes A Fungus A Fungus 1 We Seldom See The Living Parts 2 Uses Branches Of Tubing To Obtain Nutrients Ppt Download




Fungi Flashcards Quizlet



Hillis2e Ch22



Sac Fungi




The Fungi Kingdom 1 They Are Multicellular Bread Mold And Mushrooms Not Yeast Single Celled 2 They Cannot Move On Their Own 2 Main Characteristics Ppt Download




Pathogen Fungi Understanding The Similarities And Differences Of Fungi With The Other Pathogens Ppt Download



Zygote



Natural Perspective Sac Fungi Phylum Ascomycota



Fungia Archives Untamed Science




Fungus Sporophores And Spores Britannica



Fungi Humans Examples Body Parasites Used Water Process Earth




Sac Fungi Photos Animals Animals



Fungi Savannah The Cell Leader



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2



Fungi Presentation Biology



Fungi




1 Describe How Fungi Use Hyphae To Obtain




Fungi By Ava Brooks



Imperfect



Solved 23 6 Digging Deeper Co 1 Sac And Club Fungi Sac Chegg Com




Sac Fungi Black And White Stock Photos Images Alamy




16 3 Macrofungi Biology Libretexts




Fungi Concepts Of Biology



Fungi




Fungi Concepts Of Biology




Biological Diversity 4




Sac Fungi




1 Describe How Fungi Use Hyphae To Obtain




The Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Flowering Plants 78 Steps Health




Fungi Sac Fungi Yeast Molds Rusts Smuts Fungi Discover Life Mobile




Ascomycota Sac Fungi




Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Fungi




Ascomycota Advanced Ck 12 Foundation




Fungi Sac Fungi Yeast Molds Rusts Smuts Fungi Discover Life Mobile




Hillis2e Ch22




Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap



Classification And Importance Of Fungi




Kingdom Fungi The Sac Fungi



Hillis2e Ch22




Identify The Fungus Type Pictured Below A Sac Fungi B Zygote Fungi C Club Fungi D Imperfect Brainly Com




Hillis2e Ch22




Biology 2e Biological Diversity Fungi Classifications Of Fungi Opened Cuny



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms



Solved Complete Table 1 Comparing Characteristics Of Fungal Chegg Com




Fungus Chapter Ppt Video Online Download




Kingdom Fungi Acirc Euro Cent Sac Fungi Ascomycota Mycota Is Found In Fungi Acirc Euro Ldquo




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual




Fungi Lichens Office For Environmental Programs Outreach Services



Hillis2e Ch22




Identify The Fungus Type Pictured Below Club Fungi Sac Fungi Imperfect Fungi Zygote Fungi Brainly Com



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




Protists And Fungi By Brandon Howard




Phylogenetic Relations Of Fungal Phyla Adapted From Bear Et Al 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Trichoderma Leucopus A Sac Fungi From Finland Stock Photo Alamy



Fungi




Sac Fungi Photos Animals Animals




Microorganisms What Is Micro What Is An Organism



Fungi Plant Review2 Answers



Chytridiomycota



Fungi




Fungi Sac Fungi Yeast Molds Rusts Smuts Fungi Discover Life Mobile




Ascomycota Wikipedia




Ascomycota Phylum Of Fungi Britannica



Chapter 11 Protists And Fungi 7th Grade Science Kile Mingo




Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




Classification Of Fungi Mycology Microbe Notes



Vocabulary Chitin Ppt Video Online Download



Sac Fungi King Of Kingdoms




Cup Fungus Britannica




Ascomycetes High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
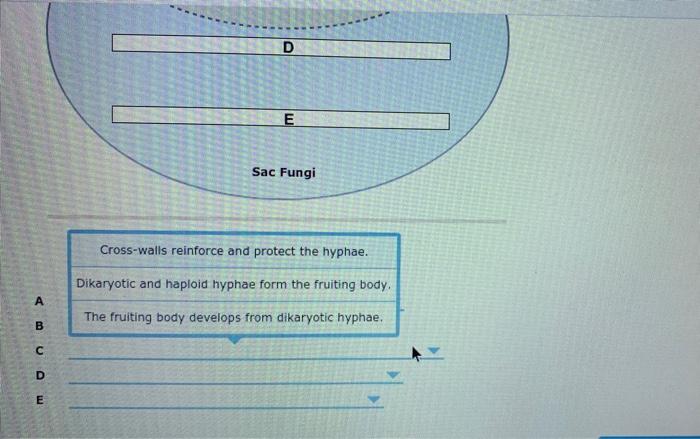



Solved 23 6 Digging Deeper Co 1 Sac And Club Fungi Sac Chegg Com




The Many Kinds Of Fungi




Heterotrophs Fungi Basics No Photosynthesis Release Enzymes To




Fungi Sac Fungi Yeast Molds Rusts Smuts Fungi Discover Life Mobile
コメント
コメントを投稿